

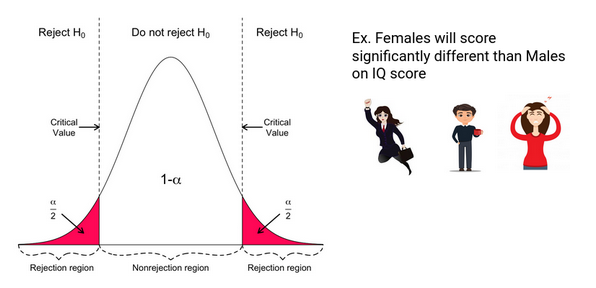
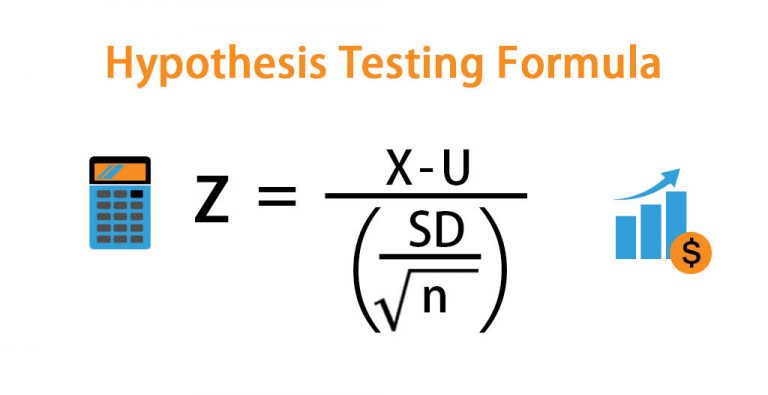
If this value falls into the middle part, then we cannot reject the null. When we calculate Z, we will get a value. Since we are conducting a two-sided or a two-tailed test, there are two cut-off lines, one on each side. How big should Z be for us to reject the null hypothesis? In all these cases, we would accept the null hypothesis. Naturally, if the sample mean is exactly equal to the hypothesized mean, Z will be 0. If the sample mean is close enough to the hypothesized mean, then Z will be close to 0. We are standardizing or scaling the sample mean we got. Z equals the sample mean, minus the hypothesized mean, divided by the standard error. Now, a test we would normally perform is the Z-test. You can see how both of them are denoted, below.Īssuming that the population of grades is normally distributed, all grades received by students should look in the following way. The alternative hypothesis is: The population mean grade is not 70%. The null hypothesis is: The population mean grade is 70%. Being the data-driven researcher that you are, you can’t simply agree with his opinion, so you start testing. The university dean believes that on average students have a GPA of 70%. Imagine you are consulting a university and want to carry out an analysis on how students are performing on average. Now that we have an idea about the significance level, let’s get to the mechanics of hypothesis testing.
So, we can choose a higher significance level like 0.05 or 0.1. Hence, a higher degree of error.įor instance, if we want to predict how much Coca Cola its consumers drink on average, the difference between 12 ounces and 12.1 ounces will not be that crucial.

However, if we are analyzing humans or companies, we would expect more random or at least uncertain behavior. So, in certain situations, we need to be as accurate as possible. If the machine pours 12.1 ounces, some of the liquid would be spilled, and the label would be damaged as well. The famous Coca Cola glass bottle is 12 ounces. As we want to be very precise, we should pick a low significance level such as 0.01. We would expect the test to make little or no mistakes. Say, we need to test if a machine is working properly. In most cases, the choice of α is determined by the context we are operating in, but 0.05 is the most commonly used value.
It is a value that we select based on the certainty we need. Typical values for α are 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1. So, the probability of making this error. The significance level is denoted by α and is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis, if it is true. However, as with any test, there is a small chance that we could get it wrong and reject a null hypothesis that is true. Normally, we aim to reject the null if it is false. What Is the Significance Level?įirst, we must define the term significance level. We assume you already know what a hypothesis is, so let’s jump right into the action. Let me know in the comments if you have any questions on $t$-test calculator for two means (unequal variances) with examples and your thought on this article.If you want to understand why hypothesis testing works, you should first have an idea about the significance level and the reject region.
#Hypothesis test calculator z cal how to#
You also learned about the step by step procedure to apply $t$-test for testing two population means and how to use $t$-test calculator for testing two population means to get the value of test statistic, p-value, and t-critical value. In this tutorial, you learned the about how to solve numerical examples on $t$-test for testing two population means with unknown and unequal variances. Step 1 - Enter the sample mean for first sample $\overline$ the null hypothesis. of Means: Test Statistics t: Degrees of Freedom: t-critical value(s): p-value: How to use $t$-test calculator for testing two means? Two tailed Calculate Results Standard Error of Diff. T test Calculator for two means Sample 1 Sample 2 Mean Standard Deviation Sample Size Variances Equal Unequal Level of Significance ($\alpha$) Tail Left tailed


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
